Making personal information safe for reuse
A range of methods can be applied to personal information to make it safe for reuse.
When using personal information for research, evaluation and other such activities, it’s important to reduce the risk that people, households, and organisations are identified without their permission.
There are different methods to make personal information safe for such reuse. Each method offers a different level of reducing the risk of re-identification.
An agency’s data does not exist in a vacuum and it may be possible to identify an individual by combining an agency’s data that has used 1 of the following methods with data available elsewhere.
AboutMyInfo — a Harvard University project — shows how easy or hard it can be to identify someone based on only on their birthdate and zip code. While using the tool requires a US zip code, there are 4 illustrative samples provided.
Aboutmyinfo.org — identity samples
How personal information can be made safe for reuse
The following methods can be used to reduce the amount of identifiable personal information contained in the individual client data that’s collected and used as part of providing public services. Other terms used include raw data, microdata, and transactional data.
Methods to use
The methods below are listed from least likelihood to greatest likelihood.
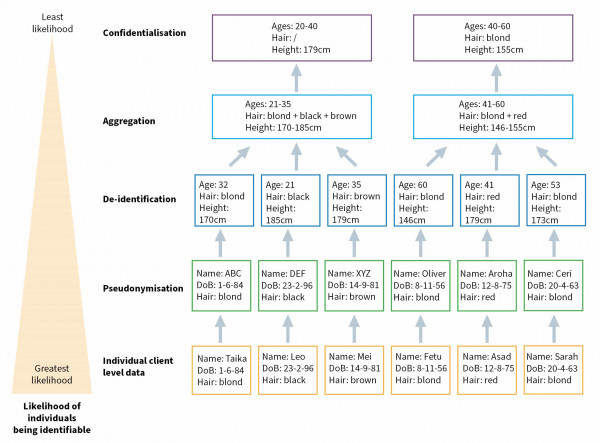
Detailed description of graph
This diagram illustrates a list of 5 methods that capture data about individuals, with each subsequent method in the list reducing the likelihood even further than the previous method of individuals being able to be identified.
The 5 methods are: individual client data, pseudonymisation, de-identification, aggregation and confidentialisation.
Here is a description of the data captured by each of these methods, starting with the method most likely to identify an individual.
- Individual client data: This method includes information about the person’s name, date of birth and hair colour.
- Pseudonymisation: This method assigns the person a different name or another way to identify them, such as assigning them a group of letters, like XYZ, along with their date of birth and hair colour.
- De-identification: This method removes the name and replaces the date of birth with their age.
- Aggregation: This method combines individual data from a group of people into age, hair and height ranges.
- Confidentialisation: This method applies statistical techniques to the data to prevent individual identification. For example, it may include the age range, and give the average height of the group, but then remove data about hair colour because an individual could be identified by it (as determined by statistical analysis).
Download — How personal information can be made safe for reuse diagram (PDF 133 KB)
More information
Utility links and page information
Last updated

